[C#과 유니티로 만드는 MMORPG 게임 개발 시리즈] Part1: C# 기초 프로그래밍 입문 강의 노트
개론
오리엔테이션
- 유니티와 언리얼 에셋 스토어에서 제공하는 무료 에셋들을 최대한 활용한다.
- 노베이스 상태에서 강의 진행
- 최종적인 목표: 500-1000명 사이의 MMORPG 인디 게임을 출시
환경 설정
- 그냥 VS와 C# 환경 설치
- installer에서 .NET 데스크톱 개발 체크.
- Visual Assist라는 어썸한 플러그인이 있으나 돈을 내야함 ㅡㅡ. 코드가 예쁘게 보인다.
데이터 갖고 놀기
정수 형식
- 주석, 정수 설명
2진수, 10진수, 16진수
- 진법 설명
정수 범위의 비밀
- 2의 보수 설명
불리언, 소수, 문자, 문자열 형식
- float 변수는 rValue에 f를 붙여줘야됨(double이 c# 기본이라)
float f = 3.14f;
- char 자료형은 1 바이트가 아니라 2 바이트다.
형식 변환
- 캐스팅 설명
데이터 연산
- 연산자 설명
비트 연산
- 최상위 비트에 1이 있는데 오른쪽 시프트 연산을 하면 최상위 비트 1은 유지된채로 시프트한다.
- 고로 이런 케이스에선 헷갈리지 않게 쓰기 위해 uint를 쓰는게 좋을 듯.
데이터 마무리
- C#에는 타입을 정하지 않고 편하게(?) 사용하는 var 자료형이 있다. 그러나 C#, C++의 장점은 타입을 명시해서 코드를 보는 사람이 명확히 이해할 수 있는 것이다. 그러므로 비추!
코드의 흐름 제어
if와 else
- if/else 설명
switch
- switch, 삼항 연산자 설명
가위-바위-보 게임
Random rand = new Random();
int aiChoice = rand.Next(0,3);
int choice = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
상수와 열거형
int ROCK = 1;
const int PAPER = 2;
switch (choice)
{
case ROCK: // ERROR!!!
~~~~~~
case PAPER: // OK!!! Because "const"
~~~~~~
}
enum Choice // 열거형
{
Rock = 1, // 기본은 0부터 시퀀스
Paper = 2,
Scissors = 0
}
static void Main(...)
{
switch (choice)
{
// 타입이 enum이므로 int로 형변환
case (int)Choice.Scissors:
Console.WriteLine("가위");
break;
....
}
}
while
do
{
bool a = true;
} while (a) // ERROR!!! 변수 a는 do 안에 {} 사이에서만 유효하므로!!
for
- for문 설명
break, continue
- break, continue 설명
함수
class Program
{
// 복사 덧셈 함수
static void CopyAddOne(int number)
{
number = number + 1;
}
// 참조 덧셈 함수
static void RefAddOne(ref int number)
{
number = number + 1;
}
static void Main(String[] args)
{
// 복사(짭퉁), 참조(진퉁)
int a = 0;
Program.CopyAddOne(a);
Console.WriteLine(a); // 출력: 0 (덧셈 안됨)
Program.RefAddOne(ref a);
Console.WriteLine(a); // 출력: 1 (덧셈 완료)
}
}
ref, out
// ref 예제
static void Swap(ref int a, ref int b)
{
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
// out 예제
static void Divide(int a, int b, out int result1, out int result2)
{
result1 = a / b;
result2 = a % b;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int num1 = 10;
int num2 = 3;
int result1;
int result2;
Divide(10, 3, out result1, out result2);
Console.WriteLine(result1); // 3
Console.WriteLine(result2); // 1
}
오버로딩
static int Add(int a, int b, int c = 0, float d = 1.0f, double e = 3.0)
{
Console.WriteLine("Add int 호출");
return a + b + c;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Program.Add(1, 2, d:2.0f) // C++는 매개변수 순서를 지켜줘야 되지만 C#은 그렇지 않아도 된다!
}
연습 문제
- 구구단 출력, 피라미드 별찍기, 팩토리얼
TextRPG
디버깅 기초
- breakpoint 조건식 검사 (‘브레이크 포인트 우클릭’ - ‘조건’)
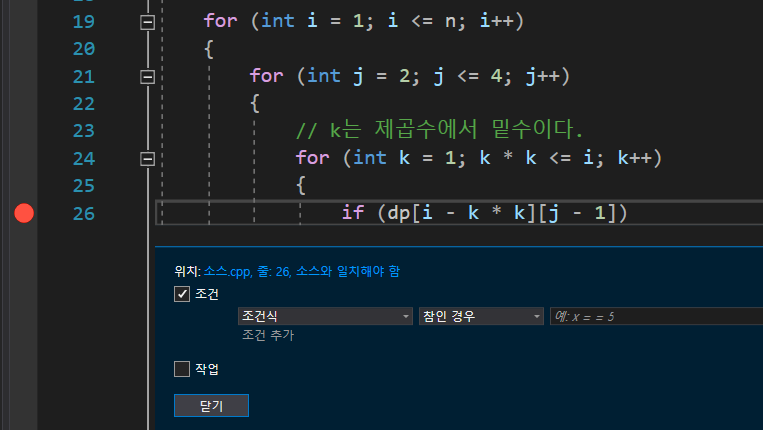
- 다음에 실행될 문 변경 (화살표를 위 아래로 드래그해서 사용)

TextRPG 직업 고르기
- enum 개념을 구글링으로 확실히 다지기!!!
TextRPG 플레이어 생성
// 주목: enum과 struct
enum ClassType
{
None = 0,
Knight = 1,
Archer = 2,
Mage = 3
}
struct Player
{
public int hp;
public int attack;
}
static void CreatePlayer(ClassType choice, out Player player) // 매개변수 주의! "out Player player"
{
// 기사, 궁수, 법사에 맞게 hp, attack 조정
switch (choice)
{
case ClassType.Knight:
player.hp = 100;
player.attack = 10;
break;
...
}
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
while(true)
{
ClassType choice = ChooseClass();
if (choice != ClassType.None)
{
Player player;
CreatePlayer(choice, out Player)
}
}
}
TextRPG 몬스터 생성
- 몬스터 관련 코딩
TextRPG 전투
- 전투 관련 코딩
객체지향 여행
객체지향의 시작
- 널 크래쉬
널인 객체의 속성 등을 호출할때 발생
복사(값)와 참조
- “struct는 복사 / class는 참조”를 해서 작업
class Knight
{
public int hp;
public int attack;
public void Move() {...}
public void Attack() {...}
}
struct Mage
{
public int hp;
public int attack;
}
class Program
{
static void KillMage(Mage mage)
{
mage.hp = 0;
}
static void KillKnight(Knight knight)
{
knight.hp = 0;
}
static void Main(...)
{
Mage mage;
mage.hp = 100;
mage.attack = 50;
KillMage(mage); // 복사이므로 이 함수를 실행해도 hp가 0으로 되지 않음
Knight knight = new Knight();
knight.hp = 100;
knight.attack = 10;
KillKnight(knight); // 참조이므로 hp가 0으로 변함
}
}
class Person
{
public string name;
public int age;
public Car car;
public string Name
{
get { return this.name; }
set { this.name = value; }
}
public int Age
{
get { return this.age; }
set { this.age = value; }
}
public Car Car
{
get { return this.car; }
set { this.car = value; }
}
public object ShallowCopy()
{
// MemberwiseClone: 새 개체를 만든 다음 현재 개체의 비정적 필드를 새 개체에 복사하여 단순 복사본을 만듬.
return this.MemberwiseClone();
}
public Object Clone()
{
Person person = new Person();
person.name = this.name;
person.age = this.age;
person.car = new Car();
person.car.model = this.car.model;
}
}
class Car
{
public string model;
public string Model
{
get { return this.model; }
set { this.model = value; }
}
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 원본 객체(person)
Person person = new Person();
person.Name = "홍길동";
person.Age = 33;
person.Car = new Car();
person.Car.Model = "뉴카이런";
// 얕은 복사된 객체(객체)
Person person2 = (Person) person.ShallowCopy();
person2.Name = "진시황";
person2.Age = 55;
person2.Car.Model = "뉴산타페":
// 두 객체 비교 - 두 객체간 동일한 Car 참조를 가지고 있다.
// WriteLine: 파라미터의 속성들을 모두 출력
// person과 person2가 동일한 뉴산타페를 가지고 있음 (그 외는 다름)
WriteLine(person);
WriteLine(person2);
// 깊은 복사된 객체
Person person3 = (Person)person.Clone();
person3.Name = "진시황";
person3.Age = 55;
person3.Car.Model = "뉴산타페";
// 두 객체 비교 - 두 객체간 서로 다른 Car 참조를 가지고 있다.
WriteLine(person);
WriteLine(person3);
}
스택과 힙
- 스택
- 불안정하고 임시적으로 사용하는 메모리
- 함수안에 변수 저장공간은 다 스택 영역에 저장된다.
- 스택에 참조 변수(주소값) -> 가리키는 본체는 힙 영역
- 힙
- 참조 타입의 본체가 있는 곳
- 동적으로 할당
- 스택 영역은 함수가 호출되고 종료되는 순간에 알아서 스케일 업/다운 하기 때문에 신경을 쓸 필요가 없다. 그러나 힙 영역은 메모리를 할당했으면 계속 메모리에 남게 된다.
- C#은 C++과는 달리 힙 영역을 프로그래머가 delete할 필요 없이 알아서 날려준다.
- 본체가 힙에만 있진 않는다. (Main 함수 변수(스택)를 ref로 선언)
생성자
public Knight()
{
hp = 100;
attack = 10;
Console.WriteLine("생성자 호출!");
}
public Knight(int hp) : this()
{
this.hp = hp;
Console.WriteLine("int 생성자 호출!");
}
// 출력
// 생성자 호출!
// int 생성자 호출!
static의 정체
- static 함수에서는 비 static 필드에 접근을 못할까?
비 static 필드의 값은 각 객체마다 다를 수 있는데 공용 static 함수에서 사용할 수 없기 때문!
Console.WriteLine() // WriteLine: Console 클래스의 static 함수
Random rand = new Random();
rand.Next(0, 2); // Next: 비 static 함수
상속성
- 상속된 클래스의 인스턴스 생성시 부모 클래스의 생성자를 먼저 호출하고 자식 클래스의 생성자를 호출한다!!
class Knight : Player
{
public Knight() : base(100) // 부모 클래스의 생성자 선택
{
base.hp = 100; // 부모 클래스의 필드 사용
}
}
- 부모 클래스의 함수도 자식 클래스의 인스턴스가 호출할 수 있다.
은닉성
- 필드를 public으로 접근 제어 하지 않고 private으로 선언 후 setter/getter로 제어하는 장점은?
- 그냥 public으로 접근 제어시 프로그램이 비대해지면 누가 필드를 변경했는지 알기 어렵다.
- set 메서드에 브레이크 포인트를 걸어서 누가 필드를 제어할려고 하는지 디버깅할때 용이
class Foo
{
int a; // 접근 지정자를 붙이지 않으면 기본 private!!
}
클래스 형식 변환
// 기본 코드 베이스
class Player
{
protected int hp;
protected int attack;
}
class Knight : Player
{
}
class Mage : Player
{
public int mp;
}
Knight knight = new Knight();
Mage mage = new Mage();
// Mage 타입 -> Player 타입 (업 캐스팅) (위험하지 않다!)
// Player 타입 -> Mage 타입 (다운 캐스팅) (될 수도 있고 안 될 수도 있고 case by case)
Player magePlayer = mage;
Mage mage2 = (Mage)magePlayer;
static void EnterGame(Player player)
{
Mage mage = (Mage)player;
mage.mp = 10; // 매개변수로 knight가 들어오면 캐스팅 실패
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Knight knight = new Knight();
Mage mage = new Mage();
EnterGame(knight);
}
// 첫 번째 해결 방법
static void EnterGame(Player player)
{
bool isMage = (player is Mage); // 핵심!
if (isMage)
{
Mage mage = (Mage)player;
mage.mp = 10;
}
}
// 두 번째 해결 방법 (추천!!!!!)
static void EnterGame(Player player)
{
Mage mage = (player as Mage); // 핵심!, 형변환 가능하면 형변환, 안되면 null
if (mage != null)
{
mage.mp = 10;
}
}
다형성
// 오버라이딩 X
class Player
{
public void Move()
{
Console.WriteLine("Player 이동!");
}
}
class Knight : Player
{
// 부모 클래스인 Player에도 Move 메서드가 있음.
// 새로 작성하기 위해 new 키워드로 선언.
public new void Move()
{
Console.WriteLine("Knight 이동!");
}
}
- 오버로딩(함수 이름의 재사용) / 오버라이딩(다형성을 이용하는것)
// 오버라이딩 O
class Player
{
public virtual void Move()
{
Console.WriteLine("Player 이동!");
}
}
class Knight : Player
{
public override void Move()
{
Console.WriteLine("Knight 이동!");
}
}
static void EnterGame(Player player)
{
// 만약 오버라이딩을 안 했다면 Player 클래스의 Move를 호출하지만
// 오버라이딩을 했다면 해당하는 타입의 클래스의(Mage)의 Move를 호출한다.
player.Move();
Mage mage = (player as Mage);
if (mage != null)
{
mage.mp = 10;
}
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Knight knight = new Knight();
Mage mage = new Mage();
EnterGame(knight);
}
override 키워드를 사용했다면 상위 클래스가 해당 메소드에 최소한 한 번은 virtual 키워드로 선언해야 한다!
class Knight : Player
{
public override void Move()
{
base.Move(); // 상위 클래스의 Move 호출
Console.WriteLine("Knight 이동!");
}
}
// C++에는 없는 C#에는 있는 문법: sealed
// Knight를 상속받는 자식들은 더이상 해당 메서드를 건들지 말아라!! 라는 뜻
class Knight : Player
{
public sealed override void Move() // 핵심
{
Console.WriteLine("Knight 이동!");
}
}
virtual로 선언한 메서드는 일반 메서드보다 성능에 더 부담을 준다.
- 가상 메소드는 일반적으로 함수 포인터가 저장되는 소위 가상 메서드 테이블(vtable)을 통해 구현된다. 이렇게 하면 실제 호출에 방향성이 추가된다. (vtable에서 호출할 함수의 주소를 가져온 다음 호출해야 함). 그러므로 성능이 더 떨어진다.
- 그러나 이것은 보통 큰 문제가 되진 않는다.
문자열 둘러보기
string name = "Harry Potter";
// 1. 찾기
bool found = name.Contains("Harry"); // true
int index = name.IndexOf('P'); // 6
int index = name.IndexOf('z'); // -1
// 2. 변형
name = name + " Junior";
string lowerCaseName = name.ToLower(); // 소문자로
string upperCaseName = name.ToUpper(); // 대문자로
string newName = name.Replace('r', 'l');
// 3. 분할
string[] names = name.Split(new char[] { ' ' });
string substringName = name.SubString(6); // Potter Junior
TextRPG2
TextRPG2 플레이어 생성
- C#은 파일 분할 시 include 작업 없이 동일 네임스페이스에서 똑같이 작업 가능하다.
- 매개변수가 있는 생성자를 만들었다면 디폴트 생성자는 더 이상 사용할 수 없다.
TextRPG2 몬스터 생성
- 구현 내용
TextRPG2 게임 진행
- 구현 내용
TextRPG2 마무리
- 구현 내용
자료구조 맛보기
배열
// foreach
int[] scores = new int[5];
foreach(int score in scores)
{
Console.WriteLine(score);
}
// 배열 초기화 3가지 방법
int[] scores = new int[5] { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 }; // 5개를 빼먹으면 에러가 뜬다!
int[] scores = new int[] { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 };
int[] scores = { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 };
연습 문제
- 디버깅시 무한 루프로 프로그램이 끝나지 않을 때 멈춰서 해당 지점을 알 수 있는 팁
- 면접 할때 Sort 알고리즘 4개 정돈 물어본다.
다차원 배열
int[,] arr = new int[2, 3];
// 2차원 배열 초기화 3가지 방법
int[,] arr = new int[2, 3] { {1,2,3}, {1,2,3} };
int[,] arr = new int[,] { {1,2,3}, {1,2,3} };
int[,] arr = { {1,2,3}, {1,2,3} };
class Map
{
int[,] tiles = {
{1,1,1,1,1},
{1,0,0,0,1},
{1,0,0,0,1},
{1,0,0,0,1},
{1,1,1,1,1}
};
public void Render()
{
var defaultColor = Console.ForegroundColor;
for (int y = 0; y < tiles.GetLength(1); y++)
{
for (int x = 0; x < tiles.GetLength(0); x++)
{
if (tiles[y,x] == 1)
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Red;
else
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Green;
Console.Write('■');
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
Console.ForegroundColor = defaultColor;
}
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Map map = new Map();
map.Render();
}
// 가변 배열
// [ . . ]
// [ . . . . . .]
// [ . . . ]
int[][] a = new int[3][];
a[0] = new int[3];
a[1] = new int[6];
a[2] = new int[2];
a[0][0] = 1;
List
- insert
O(N)
- Add
- Count가 Capacity보다 작으면 O(1)
- 새로운 요소를 수용하기 위해 용량을 늘려야하는 경우 O(N) 여기서 N은 Count
- Remove
O(N) (왜냐면 남은 요소를 shift 해야 하므로)
List<int> list = new List<int>();
// [ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
list.Add(i);
// 삽입 삭제
// [ 0, 1, 999, 2, 3, 4]
list.Insert(2, 999);
// 3이 여러개 있다면 처음 만난 3만 삭제
bool success = list.Remove(3);
list.RemoveAt(0);
list.Clear();
for (int i = 0; i< list.Count; i++)
Console.WriteLine(list[i]);
foreach (int num in list)
Console.WriteLine(num);
Dictionary
- Hashtable로 구현돼있다.
- 공이 들어있는 아주 큰 박스 [ … ] 1만개 (1~1만)
- 박스 여러개로 쪼개놓는다. [1~10] [11~20] [] [] [] [] [] [] 1천개
- 7777번 공은 어디에 있나? -> 777번째 박스에서 찾으면 된다!
- 메모리 손해
- 즉, 메모리를 내주고, 성능을 취한다!
class Monster
{
public int id;
public Monster(int id) { this.id = id; }
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Key -> Value
Dictionary<int, Monster> dic = new Dictionary<int, Monster>();
/* 삽입
dic.Add(1, new Monster(1));
dic[5] = new Monster(5);
*/
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++)
{
dic.Add(i, new Monster(i));
}
/* 위험한 코드! 해당 key에 value가 없다면? -> 크래쉬
Monster mon = dic[5000];
*/
Monster mon;
bool found = dic.TryGetValue(20000, out mon); // found: false, mon: null
dic.Remove(7777);
dic.Clear();
}
알아두면 유용한 기타 문법
Generic (일반화)
- var과 object 차이점
- var: 컴파일러가 형을 알아서 맞춰줌 ex) var -> string
- object: 진짜 형이 object
object는 참조 타입 (힙을 사용)
class MyList<T>
{
T[] arr = new T[10];
public T GetItem(int i)
{
return arr[i];
}
}
static void Test<T>(T input)
{
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Test<int>(3);
Test<float>(3.0f);
}
// T는 값 형식 이어야한다!
class MyList<T> where T : struct
{
T[] arr = new T[10];
public T GetItem(int i)
{
return arr[i];
}
}
// T는 참조 형식 이어야한다!
class MyList<T> where T : class
{
T[] arr = new T[10];
public T GetItem(int i)
{
return arr[i];
}
}
// T는 Monster, 혹은 Monster를 상속받은 클래스 이어야한다!
class MyList<T> where T : Monster
{
T[] arr = new T[10];
public T GetItem(int i)
{
return arr[i];
}
}
Interface (인터페이스)
// 추상클래스
abstract class Monster // new Monster() 불가능 (추상클래스 이므로)
{
public abstract void Shout(); // {} 같은 본문이 있으면 안됨
}
class Skeleton : Monster
{
// 에러가 뜬다!!
// 왜냐하면 상속된 추상 멤버 Shout를 구현하지 않았기 때문
}
- C#에선 다중상속을 할 수 없다. -> 인터페이스로 사용해야함
다중상속의 단점: 죽음의 다이아몬드
// 인터페이스
interface IFlyable
{
void Fly(); // 접근지정자, abstract 키워드 등을 쓸 필요없다.
}
class FlyableOrc : Orc, IFlyable
{
public void Fly() // void Fly()를 무조건 구현해야한다.
{
}
}
static void DoFly(IFlyable flyable)
{
flyable.Fly();
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
FlyableOrc orc = new FlyableOrc();
DoFly(orc);
}
interface IFace
{
void Method();
}
abstract class Face
{
public virtual void Method()
{
Console.WriteLine("Face Class 호출");
}
}
class DerivedFace : Face, IFace
{
public override void Method()
{
base.Method();
}
void IFace.Method()
{
Console.WriteLine("DerivedFace에서 IFace 오버라이딩");
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
DerivedFace df = new DerivedFace();
df.Method(); // 출력: "Face Class 호출"
// 에러
// IFace f = new IFace();
IFace f = new DerivedFace();
f.Method(); // 출력: "DerivedFace에서 IFace 오버라이딩"
}
}
Property (프로퍼티)
class Knight
{
protected int hp;
public int Hp
{
get {return hp;}
set {hp=value;}
}
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 프로퍼티
// 은닉성 보장
Knight knight = new Knight();
knight.Hp = 100;
int hp = knight.Hp;
}
public int Hp
{
get {return hp;}
private set {hp=value;} // 해당 클래스 내에만 사용가능.
void Test()
{
Hp = 100; // OK!
}
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Knight knight = new Knight();
knight.Hp = 100; // 에러!
}
// 자동 구현 프로퍼티
class Knight
{
public int Hp {get; set;}
public int Mp {get; set;} = 100; // 초기화: C# 7.0 부터 추가된 기능
}
Delegate (대리자)
-
해당 강좌에서 가장 중요함
-
콜백: 함수 자체를 인자로 넘겨준 다음에 나중에 필요로할때 안쪽에서 역으로 호출
업체 사장 - 사장님의 비서 - 우리의 연락처/용건을 받음 - 거꾸로 연락을 주세요!
delegate int OnClicked();
// delegate -> 형식은 형식인데, 함수 자체를 인자로 넘겨주는 그런 형식
// 반환: int 입력: void
// OnClicked이 delegate 형식의 이름이다!
static void ButtonPressed(OnClicked clickedFunction)
{
clickedFunction();
}
static int TestDelegate()
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello Delegate");
return 0;
}
static int TestDelegate2()
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello Delegate 2");
return 0;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// case 1
ButtonPressed(TestDelegate); // Hello Delegate가 출력됨
// case 2 Delegate Chaining
OnClicked clicked = new OnClicked(TestDelegate);
clicked += TestDelegate2;
ButtonPressed(clicked);
// 출력
// Hello Delegate
// Hello Delegate 2
}
Event (이벤트)
- delegate의 단점: delegate가 다 좋은데(?), 이 delegate를 외부에서 멋대로 호출하는 문제가 있다. -> event로 해결
// 1에서만 호출되어야 하는데 2에서도 호출이 된다
// 만약 clicked이 굉장히 중요한 정보면? -> 설계 미스
static void Main(string[] args)
{
OnClicked clicked = new OnClicked(TestDelegate);
clicked += TestDelegate2;
// 1
ButtonPressed(clicked);
// 2
clicked();
}
// InputManager.cs
// Observer Pattern
class InputManager
{
// 둘다 접근지정자를 똑같이 맞춰줘야됨
public delegate void OnInputKey();
public event OnInputKey InputKey();
public void Update()
{
if (Console.KeyAvailable == false)
return;
ConsoleKeyInfo info = Console.ReadKey();
if (info.key == ConsoleKey.A)
{
// 모두에게 알려준다!
InputKey();
}
}
}
// Program.cs
// 무한루프 돌다가 A를 누르면 "Input Received" 메시지가 출력됨!
class Program
{
static void OnInputTest()
{
Console.WriteLine("Input Received");
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
InputManager inputManager = new InputManager();
inputManager.InputKey += OnInputTest(); // 이벤트 구독
while (true)
{
inputManager.Update();
}
inputManager.InputKey(); // Error!
}
}
Lambda (람다식)
- Lambda: 일회용 함수를 만드는데 사용하는 문법이다.
enum ItemType
{
Weapon,
Armor,
Amulet,
Ring
}
enum Rarity
{
Normal,
Uncommon,
Rare
}
class Item
{
public ItemType ItemType;
public Rarity Rarity;
}
class Program
{
static List<Item> _items = new List<Item>();
delegate bool ItemSelector(Item item);
static Item FindItem(ItemSelector selector)
{
foreach (Item item in _items)
{
if (selector(item))
return item;
}
return null;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
_items.Add(new Item() {ItemType = ItemType.Weapon, Rarity = Rarity.Normal});
_items.Add(new Item() {ItemType = ItemType.Armor, Rarity = Rarity.Uncommon});
_items.Add(new Item() {ItemType = ItemType.Ring, Rarity = Rarity.Rare});
// Anonymous Function: 무명 함수 / 익명 함수
Item item = FindItem(delegate (Item item) {return item.ItemType == ItemType.Weapon;});
// or
Item item = FindItem((Item item) => {return item.ItemType == ItemType.Weapon;});
// or
ItemSelector selector = new ItemSelector((Item item) => {return item.ItemType == ItemType.Weapon;});
Item item = FindItem(selector);
}
}
class Program
{
static List<Item> _items = new List<Item>();
// 기존 ItemSelector는 item에 한정적이었지만 이 방식은 좀 더 범용적이다.
// 공용 델리게이트
delegate Return MyFunc<T, Return>(T item);
static Item FindItem(MyFunc<Item, bool> selector)...;
static Item FindItem(Func<Item, bool> selector)...;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
_items.Add(new Item() {ItemType = ItemType.Weapon, Rarity = Rarity.Normal});
_items.Add(new Item() {ItemType = ItemType.Armor, Rarity = Rarity.Uncommon});
_items.Add(new Item() {ItemType = ItemType.Ring, Rarity = Rarity.Rare});
MyFunc<Item, bool> selector = (Item item) => {return item.ItemType == ItemType.Weapon;};
Item item = FindItem(selector);
// c#에서 제공: Func
// delegate를 직접 선언하지 않아도, 이미 만들어진 애들이 존재한다.
// 반환 타입이 있을 경우: Func
// 반환 타입이 없으면: Action
Func<Item, bool> selector = (Item item) => {return item.ItemType == ItemType.Weapon;};
}
}
Exception (예외 처리)
class TestException : Exception
{
}
static void Main(...)
{
try
{
throw new TestException();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
}
finally
{
}
}
Reflection (리플렉션)
- Reflection: X-Ray
class Program
{
class Important : System.Attribute
{
string message;
public Important(string message) {this.message = message;}
}
class Monster
{
// Attribute
[Important("Very Important")]
public int hp;
protected int attack;
private float speed;
void Attack() {}
}
static void Main(...)
{
// Reflection 예제
Monster monster = new Monster();
Type type = monster.GetType();
// type.XXX 하면 많은 정보를 알 수 있음.
var fields = type.GetFields(System.Reflection.BindingFlags.Public
| System.Reflection.BindingFlags.NonPublic
| System.Reflection.BindingFlags.Static
| System.Reflection.BindingFlags.Instance);
foreach (FieldInfo field in fields)
{
string access = "protected";
if (field.IsPublic)
access = "public";
else if (field.IsPrivate)
access = "private";
// Attribute 예제
// 브레이크포인트를 걸고 확인하면 hp 필드에서
// attributes 값이 Very Important 인 것을 확인할 수 있다.
var attributes = field.GetCustomAttributes();
// public int hp와 같이 출력
Console.WriteLine($"{access} {field.FieldType.Name} {field.Name}");
}
}
}
Nullable (널러블)
class Monster
{
public int Id {get; set;}
}
static void Main(...)
{
// Nullable -> Null + able
// number에 5를 넣으면 5가 출력되고 null이면 0을 출력한다.
int? number = 5;
int b = number ?? 0;
Console.WriteLine(b);
/*-----------------------*/
Monster monster = null;
// null이 아니라면 id를 뽑아주고
// null이라면 null을 넣어주세요!
int? id = monster?.Id;
/* 위 코드와 아래 코드가 동일
if (monster == null)
id = null;
else
id = monster.Id;
*/
}